Quick Overview
Anterior Talofibular Ligament (ATFL) is a critical ligament located on the lateral (outer) side of the ankle joint. It connects the talus bone (one of the foot’s major bones) to the fibula (the smaller of the two lower leg bones). The primary function of Anterior Talofibular Ligament is to stabilize the ankle by preventing excessive forward movement of the talus bone in relation to the fibula.
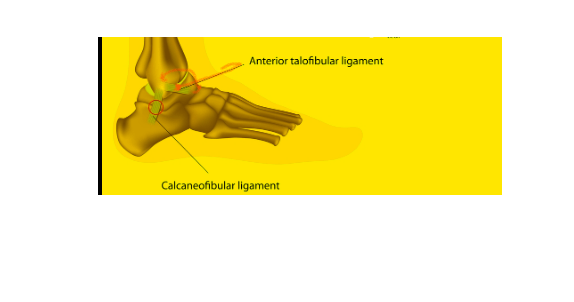
Table of Contents
Anterior Talofibular Ligament Tear
Anterior Talofibular Ligament tear is a common ankle injury, especially in athletes. ATFL tears can occur when the ankle is rolled inward, such as when landing from a jump or stepping on an uneven surface.
Read also Glenohumeral Ligaments and Radial Collateral Ligament (RCL)
Symptoms of ATFL Injury
When the Anterior Talofibular Ligament damage, it can result in a range of symptoms, including;
- Pain: Individuals often experience pain on the outer aspect of the ankle joint, particularly during weight-bearing activities or movements that stress the ligament.
- Swelling: Swelling in the affected area is a common sign of ATFL injury, indicating the body’s inflammatory response to the damage.
- Bruising: The presence of bruising around the ankle may occur, especially in cases where the injury involves significant trauma.
- Instability: The ankle may feel less stable or wobbly, making it difficult to bear weight or perform activities that require balance.
Recovery Time for ATFL Tears
The recovery time for an ATFL tear can vary depending on the severity of the injury. Mild sprains may heal in a matter of weeks, while more significant tears may require several months of rehabilitation and recovery. Physical therapy, exercises, and appropriate rest are crucial components of the recovery process.
Treatment
Treatment for Anterior Talofibular Ligament tear typically includes;
- Rest: Avoid activities that aggravate the pain, such as walking or standing for long periods of time.
- Ice: Apply ice to the injured ankle for 20 minutes at a time, several times a day.
- Compression: Wrap the injured ankle with an elastic bandage to help reduce swelling.
- Elevation: Elevate the injured ankle above the level of the heart when you are sitting or lying down.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Over-the-counter NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can help to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy can help to strengthen the muscles around the ankle and improve range of motion.
Function of (ATFL)
The primary function of the ATFL is to prevent excessive anterior or forward movement of the talus bone relative to the fibula during ankle movement. This stability is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the ankle joint and preventing injuries.
How to Prevent an ATFL Tear
There are a few things you can do to prevent an ATFL tear, including;
- Warming up before participating in physical activity
- Wearing supportive shoes
- Avoiding activities that put you at risk of ankle injuries, such as walking on uneven surfaces or playing sports that involve a lot of jumping
Questions
Q: What is the purpose of the ATFL test?
The ATFL test is used to assess the integrity of the anterior talofibular ligament. The test is typically performed in patients who have experienced an ankle injury.
Q: How is the ATFL test performed?
To perform the ATFL test, the patient lies on their back with the affected ankle extended. The examiner then grasps the patient’s heel and applies a force to invert the ankle. If the patient experiences pain or if the ankle inverts more than the uninvolved ankle, the test is considered positive.
Q: What does a positive ATFL test mean?
A positive ATFL test may indicate a sprain or tear of the anterior talofibular ligament. The severity of the injury can be determined by the degree of pain and instability experienced by the patient.
Q: What are the treatment options for an ATFL injury?
Treatment for an ATFL injury typically includes rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE). In some cases, physical therapy may be recommended to strengthen the muscles around the ankle and improve range of motion. If the injury is severe, surgery may be necessary to repair the damaged ligament.
Q: How long does it take to recover from an ATFL injury?
The recovery time for an ATFL injury depends on the severity of the injury. Most people are able to return to their normal activities within 2-6 weeks. However, some people may experience chronic ankle instability and pain for months or even years after an ATFL injury.
Q: How can I prevent an ATFL injury?
There are a few things you can do to prevent an ATFL injury, including:
1- Wearing supportive shoes with good arch support and a non-slip sole
2- Warming up before participating in physical activity
3- Avoiding activities that put you at risk of ankle injuries, such as walking on uneven surfaces or playing sports that involve a lot of jumping
