Quick Overview
Occipital triangle, also known as the omoclavicular triangle,is a discrete anatomical region situated at the base of the neck, at the intersection of the posterior cervical region and upper thorax. The occipital triangle contains a number of important structures, including the subclavian artery, vein, and plexus, as well as the lymph nodes.
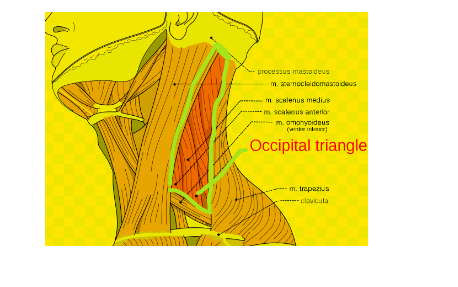
Table of Contents
Anatomy of Occipital Triangle
The Occipital Triangle derives its name from its proximity to the occipital bone and the clavicle. It is defined by specific anatomical landmarks and structures, making it distinguishable in this complex part of the body.
Read also Femoral Triangle or Iliac Fossa
Location
It is primarily located in the posterior aspect of the neck, adjacent to the upper thorax. Specifically, it resides at the confluence of the posterior triangle of the neck and the root of the upper limb.
Boundaries
It is formed by the following structures;
Anteriorly: Sternocleidomastoid muscle
Posteriorly: Trapezius muscle
Inferiorly: Inferior belly of the omohyoid muscle
Contents (Structures)
The contents of the triangle include;
- Subclavian artery: The subclavian artery is a major artery that supplies blood to the upper extremity and the brain.
- Subclavian vein: The subclavian vein is a major vein that drains blood from the upper extremity and the brain.
- Subclavian plexus: The subclavian plexus is a network of nerves that supplies motor and sensory function to the upper extremity.
- Lymph nodes: The occipital triangle contains a number of lymph nodes, which are part of the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system helps to fight infection.
Associated Condition
The occipital triangle is associated with a number of medical conditions, including:
- Occipital neuralgia: Occipital neuralgia is a type of headache that is caused by inflammation or compression of the occipital nerves.
- Suboccipital myofascial pain syndrome: Suboccipital myofascial pain syndrome is a condition that is characterized by pain and stiffness in the muscles of the neck and upper back. It is often associated with trigger points, which are small, painful knots in the muscles.
- Occipital artery aneurysm: An occipital artery aneurysm is a bulge in the wall of the occipital artery. It is a relatively rare condition, but it can be life-threatening if it ruptures.
- Occipital artery dissection: An occipital artery dissection is a tear in the lining of the occipital artery. It is also a relatively rare condition, but it can cause a stroke if it blocks the flow of blood to the brain.
- Occipital triangle lymphadenopathy: Occipital triangle lymphadenopathy is enlargement of the lymph nodes in the occipital triangle. It can be caused by a variety of conditions, including infection, inflammation, and cancer.
Clinical Significance
The occipital triangle is an important region of the neck that contains a number of important structures. Damage to the structures in the occipital triangle can lead to serious problems, such as stroke, paralysis, and lymphedema.
Questions
Q: What are the symptoms of a subclavian artery thrombosis?
The symptoms of a subclavian artery thrombosis include pain in the arm, numbness and weakness in the arm, and decreased blood flow to the arm.
Q: What are the symptoms of a subclavian artery aneurysm?
The symptoms of a subclavian artery aneurysm include pain in the neck and arm, as well as other symptoms such as pulsation in the neck and difficulty swallowing.
Q: What are the symptoms of a subclavian vein thrombosis?
The symptoms of a subclavian vein thrombosis include pain in the arm, swelling in the arm, and decreased blood flow to the arm.
Q: What are the symptoms of a subclavian vein aneurysm?
The symptoms of a subclavian vein aneurysm include pain in the neck and arm, as well as other symptoms such as pulsation in the neck and difficulty swallowing.
Q: What are the symptoms of scalene muscle syndrome?
The symptoms of scalene muscle syndrome include pain in the neck and arm, as well as other symptoms such as numbness and weakness in the arm.
