Quick Overview
Supraspinatus tendon is one of the four rotator cuff tendons, which are a group of tendons that attach the muscles of the rotator cuff to the humerus (upper arm bone). It connects the supraspinatus muscle to the greater tuberosity of the humerus. The supraspinatus muscle is responsible for raising the arm overhead.
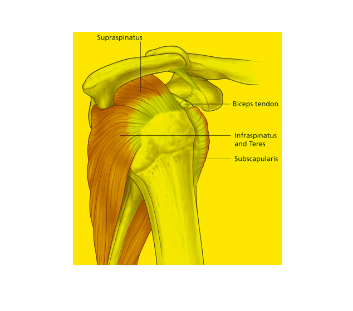
Table of Contents
Anatomy of Supraspinatus Tendon
This tendon arises from the supraspinatus muscle, one of the four rotator cuff muscles, and inserts onto the greater tubercle of the humerus (upper arm bone). This tendon plays a crucial role in lifting the arm and rotating it outward.
Supraspinatus Tendon Tear
It is the most common type of rotator cuff tear. It can be partial or complete. Partial tears are more common and typically occur in people over the age of 40. Complete tears are less common and typically occur in athletes or people who have had a traumatic injury to the shoulder.
Symptoms
Common symptoms include:
- Pain in the front or top of the shoulder
- Weakness in the shoulder, especially when raising the arm overhead
- Difficulty sleeping on the affected side
- A popping or snapping sensation in the shoulder
Supraspinatus Tendonitis
Tendonitis is an inflammation of the supraspinatus tendon. It is a common condition that can occur in people of all ages. It can be caused by overuse of the shoulder, such as from sports or repetitive activities. It can also be caused by a traumatic injury to the shoulder.
Read also Triceps Tendon and Patellar Tendon
Causes
This condition is most commonly caused by overuse of the shoulder. This can occur from sports, such as swimming, tennis, and baseball. It can also occur from repetitive activities, such as painting, carpentry, and lifting heavy objects. Other possible causes include
- Age: It is more common in people over the age of 40.
- Trauma: A traumatic injury to the shoulder, such as a fall or a car accident, can cause supraspinatus tendonitis.
- Bone spurs: Bone spurs are bony growths that can form on the bones of the shoulder joint. They can irritate the supraspinatus tendon and cause inflammation.
- Impingement syndrome: Impingement syndrome is a condition in which the rotator cuff tendons are pinched between the humerus and the acromion (a bony projection on the scapula). Impingement syndrome can cause supraspinatus tendonitis.
Signs and Symptoms
The most common sign and symptom is pain in the front or top of the shoulder. The pain is typically worse with movement, especially when raising the arm overhead. Other signs and symptoms include;
- Tenderness in the shoulder
- Swelling in the shoulder
- Difficulty raising the arm overhead
- Crepitus (a popping or grinding sensation) in the shoulder
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is based on the physical examination and medical history. Imaging tests, such as an ultrasound or MRI, may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis and assess the severity of the injury.
Treatment
Treatment option typically involves rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE). Physical therapy may also be recommended to help strengthen the rotator cuff muscles and improve range of motion. In some cases, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or corticosteroid injections may be prescribed to help reduce pain and inflammation.
If conservative treatment is not effective, surgery may be considered to repair the supraspinatus tendon. However, surgery is rarely necessary.
Prevention
The best way to prevent this condition is to avoid overuse of the shoulder. This can be done by gradually increasing the intensity and duration of your workouts, and by taking breaks from repetitive activities. Other things you can do to help prevent supraspinatus tendonitis include:
- Warm up before exercise and cool down afterwards
- Stretch your rotator cuff muscles regularly
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Use proper lifting techniques
If you experience any pain in your shoulder, it is important to see a doctor to get a diagnosis and treatment plan.
Questions
Q: How long does supraspinatus tendonitis take to heal?
The healing time for supraspinatus tendonitis varies depending on the severity of the injury and the individual’s healing process. Most people recover within 6 weeks to 3 months, but some people may take longer.
Q: What are the risks of supraspinatus tendonitis surgery?
The risks of supraspinatus tendonitis surgery include infection, bleeding, nerve damage, and wound healing problems. In rare cases, the tendon may rupture again after surgery.
Q: What can I do to prevent supraspinatus tendonitis?
To help prevent supraspinatus tendonitis, you can:
1- Avoid overuse of the shoulder.
2- Gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts.
3- Take breaks from repetitive activities.
4- Warm up before exercise and cool down afterwards.
5- Stretch your rotator cuff muscles regularly.
6- Maintain a healthy weight.
7- Use proper lifting techniques.
Q: What is the best way to treat supraspinatus tendonitis?
The best way to treat supraspinatus tendonitis depends on the severity of the injury. In most cases, treatment includes rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE). Physical therapy may also be recommended to help strengthen the rotator cuff muscles and improve range of motion. In some cases, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or corticosteroid injections may be prescribed to help reduce pain and inflammation.
Q: What are the long-term complications of supraspinatus tendonitis?
Long-term complications of supraspinatus tendonitis include:
1- Chronic pain
2- Weakness in the shoulder
3- Stiffness in the shoulder
4- Recurrence of tendonitis
