Quick Overview
What is Zygomaticus Major Muscle? The Zygomaticus Major muscle, often called the “smile muscle,” responsible for raising the corner of the mouth forming a smile.
The zygomaticus major muscle is attached to the zygomatic bone at the cheekbone and to the corner of the mouth. It is innervated by the facial nerve and supplied blood by the facial artery.
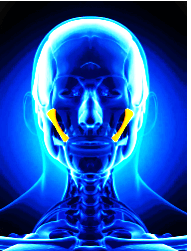
Table of Contents
Anatomy
The Zygomaticus Major is a paired muscle located on each side of the face. It extends from the zygomatic bone (cheekbone) to the corner of the mouth, allowing for precise control of the smile.
| Muscle | Description |
| Origin | Zygomatic bone |
| Insertion | Corner of the mouth, blends with the levator anguli oris muscle |
| Blood Supply | Facial artery |
| Nerve Supply | Facial nerve |
| Function | Raises the corner of the mouth, forming a smile |
Location:
This muscle is situated in the midface region, starting from the cheekbone and extending diagonally towards the corner of the mouth. It is crucial for elevating the corners of the lips during smiling.
Function
The primary function of the Zygomaticus Major muscle is to facilitate the formation of smiles by elevating the corners of the mouth. When this muscle contracts, it creates the characteristic “upward” movement of the lips associated with happiness and joy.
Nerve Supply:
It is innervated by the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII), which carries the signals needed for muscle contraction and the formation of smiles.
Blood Supply:
Blood supply to the Zygomaticus muscle is provided by branches of the facial artery, ensuring it receives the oxygen and nutrients necessary for optimal function.
Common zygomaticus major muscle issues include:
- Bell’s palsy: Bell’s palsy is a temporary paralysis of the facial nerve. It can cause weakness or paralysis of the muscles on one side of the face, including the zygomaticus major muscle.
- Stroke: A stroke can damage the facial nerve, which can lead to weakness or paralysis of the muscles in the face, including the zygomaticus major muscle.
- Myasthenia gravis: Myasthenia gravis is a chronic autoimmune disease that causes weakness of the muscles. It can affect any muscle in the body, including the zygomaticus major muscle.
Exercises for Zygomaticus Major Muscle:
Maintaining the health and strength of the Zygomaticus Major muscle is essential for a radiant and genuine smile. Here are some exercises to consider incorporating into your daily routine:
1- Smile Widening:
- Smile as wide as you can while keeping your lips together.
- Hold the smile for a few seconds.
- Repeat this exercise several times to strengthen and tone the Zygomaticus Major muscles.
2- Cheek Lifts:
- Place your fingertips at the corners of your mouth.
- Gently lift the corners of your mouth towards your eyes, creating a smile.
- Hold for a few seconds and release.
- Repeat this exercise to enhance the muscle’s strength and flexibility.
3- Mirror Practice:
- Stand in front of a mirror and practice smiling naturally.
- Pay attention to the movement of the Zygomaticus Major muscles.
- This exercise helps you become more aware of your smile and its symmetry.
Questions
1- How does the Zygomaticus Major muscle contribute to facial expressions and emotional communication?
This muscle plays a pivotal role in facial expressions, particularly in conveying happiness and joy. Its contraction elevates the corners of the mouth, creating a smile that expresses positive emotions.
2- What causes smile asymmetry, and can exercises help improve it?
Smile asymmetry can result from differences in the strength or function of the Zygomaticus muscles. Exercises targeting these muscles, such as smile widening and cheek lifts, can help improve symmetry over time.
3- Can issues with the Zygomaticus Major muscle affect one’s ability to smile symmetrically?
Yes, issues such as muscle weakness or fatigue in the Zygomaticus muscle can lead to asymmetrical smiles, impacting one’s confidence in their facial expressions.
4- Are there exercises to strengthen the Zygomaticus Major muscle and improve smile symmetry?
Yes, exercises like “smile widening” and “cheek lifts” can help strengthen the Zygomaticus muscle and promote more symmetrical and expressive smiles.
5- What role does the Zygomaticus Major muscle play in non-verbal communication and social interactions?
This muscle is vital in non-verbal communication, as it allows us to convey positive emotions, connect with others, and establish rapport through genuine and inviting smiles.
