Table of Contents
Quick Overview
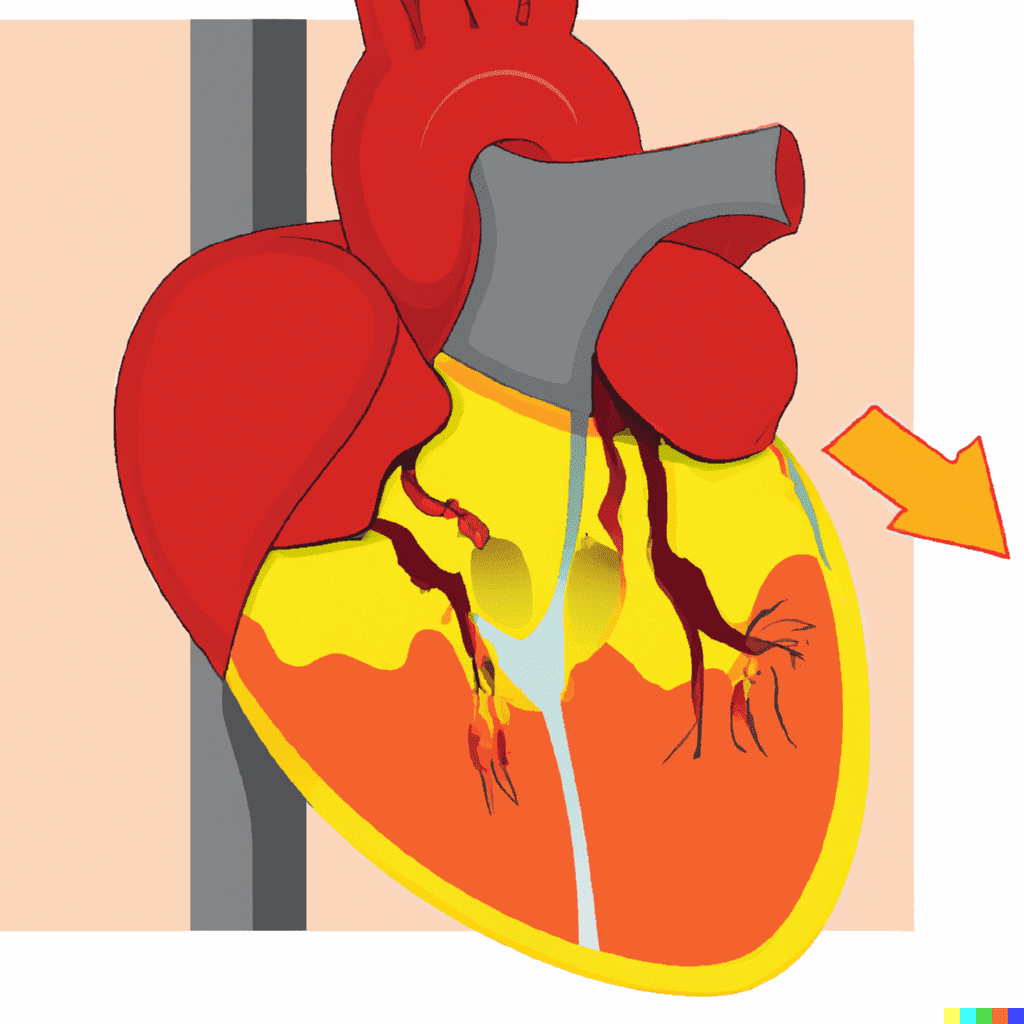
The term ‘’Beck’s Triad’’ is a set of three clinical signs that are commonly associated with cardiac tamponade, a potentially life-threatening condition in which excess fluid accumulates within the pericardium, the membrane surrounding the heart.
It was first described by an American cardiothoracic surgeon named ‘’Claude Beck’’. The triad includes low blood pressure, distant or muffled heart sounds, and jugular venous distension.
These three signs are important diagnostic indicators on the basis of which the medical professionals identify cardiac tamponade in patients.
The main cause of low blood pressure is the accumulation of excess fluid in the pericardium (membrane of the heart is called pericardium) that compresses the heart, and reduces its ability to pump blood effectively.
The distant heart sound (also called muffled heart sound) is the result of the same compression and is often heard during the physical examination of the heart.
The Jugular venous distention is caused by an increase of pressure in the jugular veins, which can be seen in the neck and is another indication of cardiac tamponade.
The cardiac tamponade can lead to a life-threatening condition, If left untreated, making it essential to recognize the signs of Beck’s Triad as early as possible.
The timely identification of these clinical signs helps the doctors to diagnose and treat the underlying condition promptly, potentially saving the patient’s life.
Symptoms of Beck’s Triad
Beck’s triad is characterized by three classic clinical signs, which are given as:
1. Low Blood Pressure
Low blood pressure is one of the most common symptoms of Beck’s triad. In mild cases the patient may experience dizziness, lightheadedness, and confusion, while In severe cases, symptoms get worse and the patient may go into shock, which can be life-threatening.
2. Jugular Venous Distension
Another classic sign of Beck’s triad is jugular venous distension, which occurs when the jugular veins in the neck become enlarged and bulge out due to high pressure. This is a result of increased pressure in the right side of the heart.
3. Muffled Heart Sounds
The third classic sign of Beck’s triad is muffled heart sounds. The sound of the heart beating becomes softer and less distinct. This is because the fluid surrounding the heart muffles the sound.
Causes of Beck’s Triad
The most common cause of Beck’s triad is cardiac tamponade. This occurs when fluid accumulates within the pericardium, the sac that surrounds the heart. The fluid can be blood, pus, or lymphatic fluid. Other causes of Beck’s triad include:
- Trauma to the chest.
- Cancer that has spread to the pericardium.
- Infections such as tuberculosis or viral pericarditis.
- Autoimmune diseases such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis.
Diagnosis of Beck’s Triad
To diagnose Beck’s triad, the doctor will perform a physical examination and order several tests, such as;
1- Electrocardiogram (ECG): This is a test which measures the electrical activity of the heart and can show if the heart is being compressed.
2- Chest X-ray: This can be performed to see if there is any fluid around the heart.
3- Echocardiogram: This test uses ultrasonic waves to create an image of the heart and can show if there is any fluid around the heart.
4- CT or MRI: These tests can provide a detailed image of the heart and can help identify any abnormalities or fluid buildup around the heart.
Treatment of Beck’s Triad
Beck’s triad is a medical emergency that requires prompt treatment to prevent further complications. The primary treatment for cardiac tamponade is to lower the pressure by removing the fluid that is compressing the heart.
This is usually done by inserting a needle into the pericardium and draining the fluid. In some cases, a surgical procedure called a pericardiocentesis may be necessary to remove the fluid.
Prevention of Beck’s Triad
There are no specific measures to prevent Beck’s triad. However, prompt treatment of underlying medical conditions such as infections or autoimmune diseases may reduce the risk of developing cardiac tamponade.
In addition, avoiding trauma to the chest and seeking medical attention immediately if chest trauma occurs can help prevent Beck’s triad.
Comparison between Beck’s Triad and Cushing’s Triad
| Beck’s Triad | Cushing’s Triad | |
| Definition | A set of three classic signs indicating cardiac tamponade, including low blood pressure, jugular venous distension, and muffled heart sounds. | A set of three classic signs indicating increased intracranial pressure, including hypertension, bradycardia, and irregular respirations. |
| Causes | Cardiac tamponade resulting from fluid accumulation in the pericardium. | Increased intracranial pressure resulting from brain injury, tumor, or bleeding. |
| Clinical Presentation | Low blood pressure, jugular venous distension, and muffled heart sounds. | Hypertension, bradycardia, and irregular respirations. |
| Diagnostic Tests | Echocardiogram to detect pericardial effusion. | CT or MRI scan to detect brain injury, tumor, or bleeding. |
| Treatment | Pericardiocentesis to remove the fluid. | Treatment of the underlying cause of increased intracranial pressure. |
| Prognosis | Prompt treatment can improve the chances of a positive outcome. | The prognosis depends on the underlying cause and how quickly it is diagnosed and treated. |
Scenario Question:
A 45-year-old male patient named John presents to the emergency department with chest pain, shortness of breath, and dizziness. Upon examination, you observed that the patient’s blood pressure is 80/50 mmHg, and heart sounds are muffled. The patient reports recent trauma to the chest. An echocardiogram reveals pericardial effusion.
Question:
Based on the patient’s presentation and diagnostic results, what is the likely diagnosis, and what is the appropriate treatment?
Beck’s Triad MCQ’s
1- What is Beck’s triad?
A) A set of three classic signs indicating increased intracranial pressure
B) A set of three classic signs indicating cardiac tamponade
C) A set of three classic signs indicating hypoglycemia
D) A set of three classic signs indicating hyperthyroidism
Answer: B
2- Which one is NOT the clinical manifestation of Beck’s triad?
A) Low blood pressure
B) Jugular venous distension
C) Muffled heart sounds
D) Bradycardia
Answer: D
3- Which method is commonly used for Beck’s triad diagnosis?
A) CT or MRI scan
B) Echocardiogram
C) Electrocardiogram
D) Chest X-ray
Answer: B
4- What is the treatment for Beck’s triad?
A) Treatment of the underlying cause of increased intracranial pressure
B) Pericardiocentesis to remove the fluid
C) Administration of corticosteroids
D) Surgical intervention
Answer: B
5- Which of the following conditions can cause Beck’s triad?
A) Brain injury
B) Pulmonary embolism
C) Cardiac tamponade
D) A and C
Answer: D
Related Articles
Calot’s triangle: Anatomy, Contents, Boundaries – HealthandPhysioTalar Tilt Test: Performance, Diagnosis, Treatment, Importance