Quick Overview
The subtalar fossa is a narrow space located between the talus and calcaneus bones of the foot. It is filled with fluid and contains a number of ligaments, tendons, and nerves. The subtalar fossa is an important part of the foot joint complex, allowing for inversion and eversion of the foot.
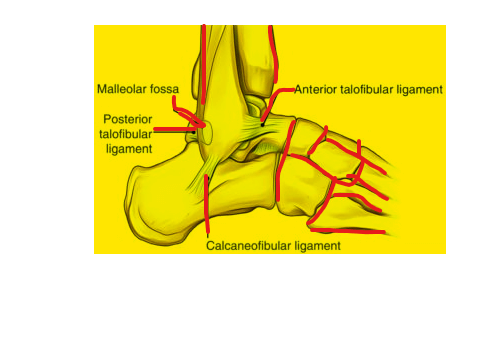
Table of Contents
Anatomy of Subtalar Fossa
The subtalar fossa is a triangular-shaped cavity that is divided into two parts, i,e the anterior subtalar fossa and the posterior subtalar fossa. The anterior subtalar fossa is located between the talus and calcaneus bones, while the posterior subtalar fossa is located between the talus and the navicular bone.
Also read Hypophyseal Fossa and Middle Cranial Fossa
Location
The subtalar fossa is located on the inferior surface of the talus bone and the superior surface of the calcaneus bone. It is located in the hindfoot, between the talonavicular joint (in front) and the calcaneonavicular joint (behind).
Boundaries
It is bounded by the following structures:
Anteriorly: Talonavicular joint
Posteriorly: Calcaneonavicular joint
Medially: Sustentaculum tali
Laterally: Sinus tarsi
Structures
The structures here are;
- Talocalcaneal joint capsule: The talocalcaneal joint capsule is a thin, fibrous sac that surrounds the talocalcaneal joint. It helps to stabilize the joint and prevent excessive movement.
- Talocalcaneal interosseous ligament: The talocalcaneal interosseous ligament is a strong ligament that connects the talus and calcaneus bones. It helps to stabilize the joint and prevent excessive movement.
- Sinus tarsi: The sinus tarsi is a narrow passageway located between the talus and calcaneus bones. It contains the talocalcaneal joint capsule and the talocalcaneal interosseous ligament.
- Tarsal canal: The tarsal canal is a narrow passageway located between the talus and calcaneus bones. It contains the posterior tibial nerve and vessels.
Clinical Significance
The subtalar fossa is an important part of the ankle joint, and it plays a role in stabilizing the joint and allowing for movement of the foot. However, the subtalar fossa is also susceptible to a number of injuries and conditions, which include;
- Subtalar joint sprain: A subtalar joint sprain is an injury to the ligaments that support the subtalar joint. It is caused by excessive movement of the joint.
- Subtalar joint arthritis: Subtalar joint arthritis is a condition that causes degeneration of the cartilage in the subtalar joint. It can be caused by aging, injury, or overuse.
- Subtalar joint instability: Subtalar joint instability is a condition in which the subtalar joint is loose and unstable. It can be caused by injury, overuse, or certain medical conditions.
Associated Conditions
The following conditions are associated with the subtalar fossa:
- Subtalar joint sprain
- Subtalar joint arthritis
- Subtalar joint instability
- Calcaneal fracture
- Tarsal tunnel syndrome
Subtalar Fossa Treatment
The treatment for subtalar fossa injuries and conditions depends on the severity of the injury or condition. Some common treatment options may include;
- Rest
- Ice
- Compression
- Elevation
- Physical therapy
- Medications
- Surgery
Prevention
The following tips can help to prevent subtalar fossa injuries and conditions;
- Warm up before exercising
- Wear supportive shoes
- Avoid overuse of the subtalar joint
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Stretch regularly
- Strengthen the muscles around the ankle and foot
Questions
Q: What are the symptoms of a subtalar joint sprain?
The symptoms of a subtalar joint sprain include pain, swelling, and tenderness in the subtalar fossa. You may also have difficulty moving your foot and ankle.
Q: What are the risk factors for a subtalar joint sprain?
The risk factors for a subtalar joint sprain include:
1- Participating in sports that involve high-impact activities, such as running, jumping, and basketball
2- Wearing shoes that do not provide adequate support
3- Having a history of subtalar joint injuries
Q: How is a subtalar joint sprain diagnosed?
A subtalar joint sprain is typically diagnosed based on a physical examination and medical history. Your doctor may also order imaging tests, such as an X-ray or MRI, to confirm the diagnosis and assess the severity of the injury.
Q: How is a subtalar joint sprain treated?
The treatment for a subtalar joint sprain depends on the severity of the injury. Treatment options may include:
1- Rest
2- Ice
3- Compression
4- Elevation
5- Physical therapy
6- Medications
7- Surgery
Q: What is the prognosis for a subtalar joint sprain?
The prognosis for a subtalar joint sprain is generally good. Most people make a full recovery within a few weeks. However, some people may experience long-term problems, such as pain and instability.
