Quick Overview
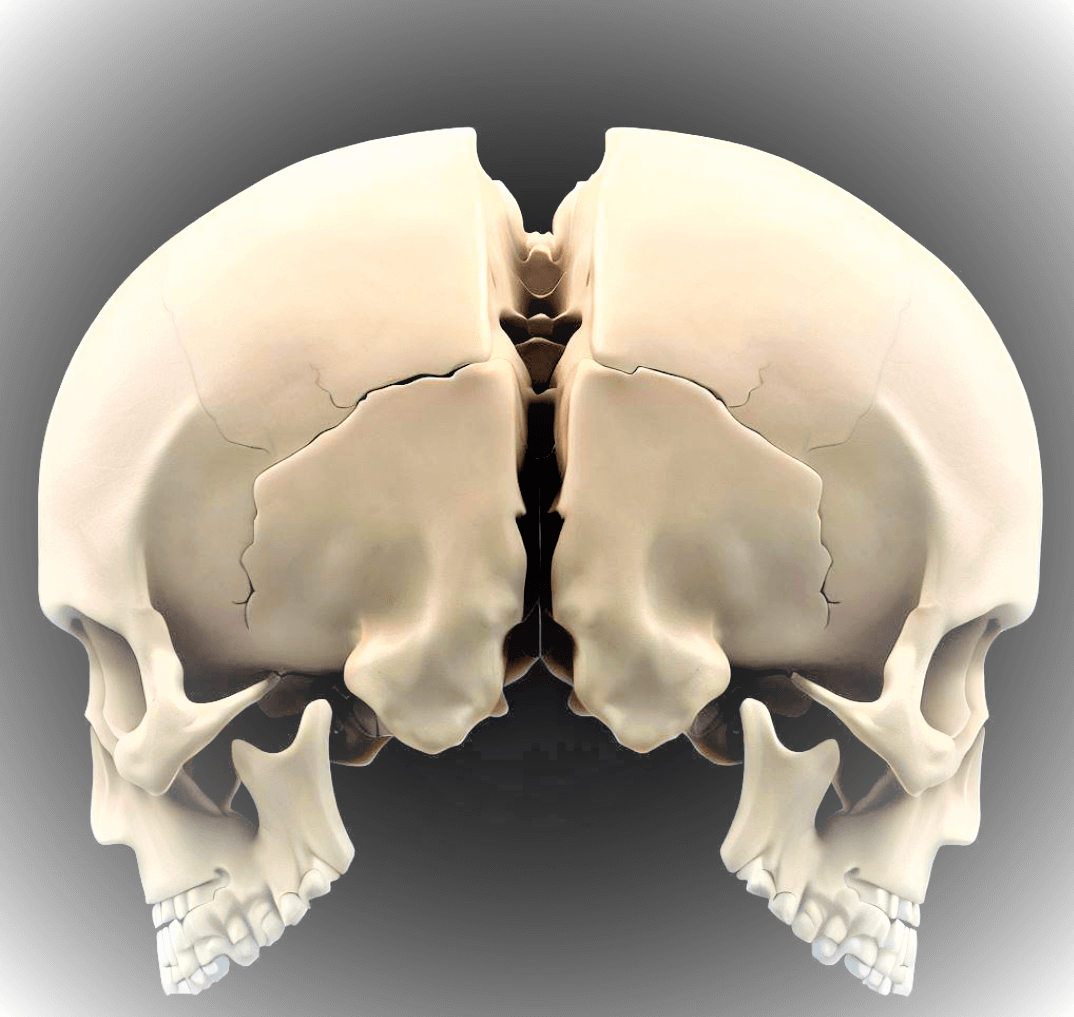
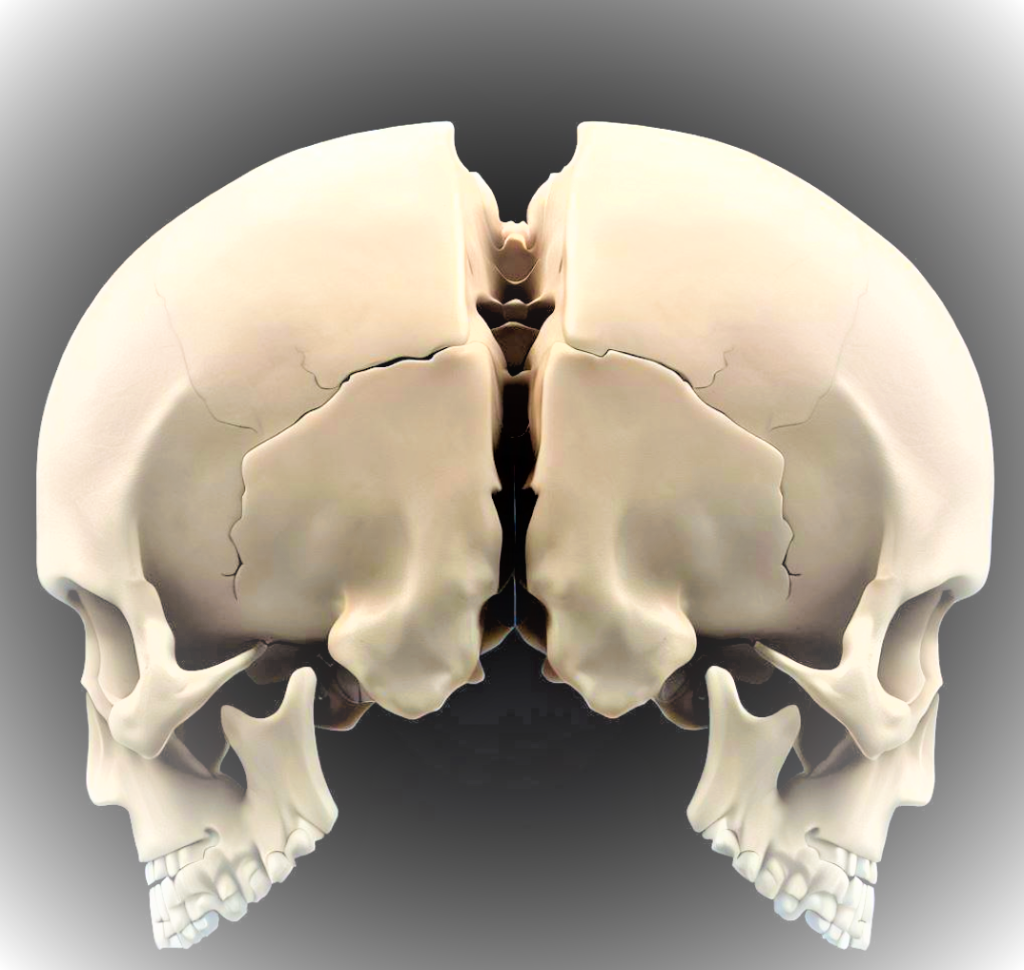
The parietal bones are two flat bones that form the upper sides and back of the skull. They are located on either side of the sagittal suture, which is the midline ridge that runs from front to back of the skull.
The parietal bones are important for protecting the brain and providing structural support for the skull and also play a role in forming the cranial cavity, which is the space that houses the brain.
Table of Contents
I. Anatomy of the Parietal Bones
A. External Features
It possess several distinguishing external features like the parietal eminence, which is a slight elevations on the surface and contribute to the skull’s characteristic contour.
Temporal lines mark the attachment points for various muscles, while the sagittal suture connects the two parietal bones at the midline of the skull.
| Feature | Description |
| Parietal Eminence | Slight elevations on the surface of bones |
| Temporal Lines | Muscle attachment points on the sides |
| Sagittal Suture | Connects the two parietal bones at midline |
B. internal Features
Internally, it contain parietal foramina i,e small openings that allow the passage of blood vessels. Additionally, grooves accommodate blood vessels’ pathways, further contributing to the intricate vascular network within the skull.
| Feature | Description |
| Parietal Foramina | Small openings for blood vessel passage |
| Grooves for vessels | Pathways for the intricate vascular network |
II. Functions
A. Protection of Brain
These bones form a robust cranial vault, providing exceptional protection to the brain from external impacts. Together with other cranial bones, they create a secure fortress for this vital organ.
B. Structural Support
These bones contribute to the overall structural integrity of the skull, ensuring stability and shape. They also aid in supporting facial bones, creating a cohesive structure for our intricate features.
C. Cranial Cavity Formation
These bones also participate in shaping the cranial cavity, which houses the brain and its protective membranes. Their positioning influences the overall volume and shape of the cranial cavity.
III. Developmental and Evolutionary Aspects
A. Formation during Fetal Development
The parietal bones originate from separate ossification centers during fetal development. Over time, these centers fuse, forming the solid bones we have in adulthood. This process exemplifies the intricate nature of human growth.
B. Evolutionary Significance
Throughout the course of human evolution, changes in the shape and size of the parietal bones have been observed, reflecting adaptations and developments in our species.
IV. Common Conditions and Disorders
A. Fractures
Traumatic accidents can lead to bone fractures, which require immediate medical attention and treatment.
B. Abnormalities and Developmental Issues
In some cases, individuals may have congenital abnormalities affect the development of these bones leading to various challenges.
V. Diagnostic Techniques and Imaging
- X-rays: X-rays can be used to visualize the structure of these bones and to detect any fractures or other abnormalities.
- CT scans: CT scans provide detailed images of these bones and can be used to diagnose a variety of conditions, such as fractures, sinusitis, and tumors.
- MRI scans: MRI scans provide even more detailed images of bones than CT scans. They can be used to diagnose a variety of conditions, such as brain tumors and vascular abnormalities.
VI. Surgical Procedures
A. Bone Reconstruction
Severe trauma or congenital deformities may necessitate surgical reconstruction to restore both functionality and appearance.
B. Cranioplasty
Cranioplasty involves repairing or replacing damaged portions of the cranial vault, which may involve these bones also.
VII. Interesting Facts
A. Role in Determining Age in Forensic Sciences
Parietal bones, along with other cranial features, are valuable in determining a person’s age in forensic investigations.
B. Historical and Cultural Significance
Throughout history, these bones have held cultural and historical significance, finding their place in various rituals and art forms.
Questions
1. What are parietal bones?
Parietal bones are two large, flat bones located at the top and sides of the human skull, forming part of the cranial vault.
2. What is the function of parietal bones?
Parietal bones have multiple functions: they protect the brain from external impacts, provide structural support to the skull, and contribute to the formation of the cranial cavity.
3. What are the external features of parietal bones?
The external features of parietal bones include parietal eminences (slight elevations on the surface), temporal lines (muscle attachment points on the sides), and the sagittal suture (connecting both parietal bones at the midline).
4. How do parietal bones develop during fetal growth?
Parietal bones form from separate ossification centers during fetal development. Over time, these centers fuse, resulting in the solid bones present in adulthood.
5. What medical imaging techniques are used to assess parietal bone issues?
Medical professionals utilize X-rays and CT scans for diagnosing parietal bone fractures and related conditions. MRI scans provide detailed images, offering comprehensive insights into parietal bone-related issues and surrounding structures.
Related Articles:
Frontal Bone: Anatomy, Functions, Location, 2 Facts
Triángulo posterior del cuello : bordes, contenido, divisiones, nemotecnia
Read more

Reading from US thanks for such a helpful content