Quick Overview:
The frontal bone is a vital component of the human skull, holds a position of utmost importance. It is located at the front of the cranium, and play a crucial role in safeguarding the brain and shaping of our facial structure.
Table of Contents
II. Anatomy
A. External Features
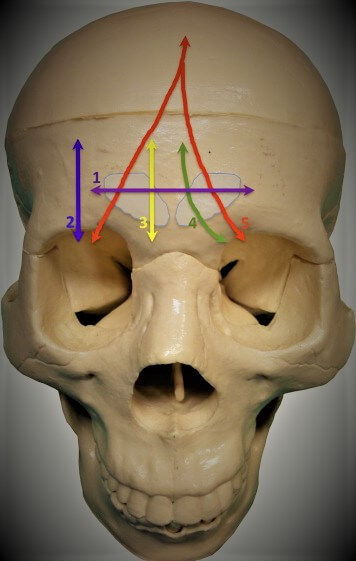
Frontal Eminences: It exhibits frontal eminences, subtle prominences on the forehead that contribute to individual facial characteristics.
Supraorbital Foramina/Notches: Positioned above the eyes, these tiny openings serve as passageways for blood vessels and nerves, enabling sensory functions.
Glabella: The smooth area between the eyebrows which adds to the bone’s distinctive features, marking a prominent landmark on the forehead.
Superciliary Arches: The arches located above the eyes lend additional structure and aesthetic appeal to the human face.
B. Internal Features
Frontal Sinuses: Inside the bone lies frontal sinuses, which are air-filled spaces responsible for the resonance during speech and reducing the weight of the skull.
Orbital Plate: It forms a part of the eye sockets, the orbital plate provides support for the eyes and surrounding structures.
Crista Galli: This bony ridge serves as an attachment point for the protective covering of the brain, known as the meninges.
II. Functions:
1. Brain Protection: The main function of this bone is to safeguards the most critical organ in our body, the brain, against the potential injuries from external forces.
2. Facial Structure: Together with other facial bones, it contributes to defining the unique appearance of an individual face.
3. Cranial Cavity Contribution: This bone forms the anterior portion of the cranial cavity, and also provide support and stability.
III. Developmental and Evolutionary Aspects:
The frontal bone begins to develop during the embryonic stage as two separate bones, which fuse together during childhood and continue to grow throughout the childhood and adolescence, reaching its full size by adulthood.
It is relatively complex bone, and its development has been the subject of much research. Scientists believe that it may have evolved from a single bone in early vertebrates. Also thought to have played an important role in the evolution of human facial features.
IV. Common Conditions and Disorders:
The bone is susceptible to a number of conditions and disorders, including:
- Fractures: These are common injuries that can occur as a result of falls, car accidents, or other traumatic events.
- Frontal sinusitis: This is an inflammation of the frontal sinuses, which are air-filled cavities that are located within the frontal bone.
- Congenital abnormalities: It can be affected by a number of congenital abnormalities, such as holoprosencephaly, which is a rare disorder that results in the incomplete development of the brain.
VI. Diagnostic and Imaging Techniques
A. X-rays and CT Scans: Medical professionals use X-rays and CT scans to diagnose frontal bone fractures and to assess sinus conditions effectively.
B. MRI Scans: Providing detailed images, MRI scans help gain comprehensive insights into frontal bone-related issues and associated structures.
C. Importance in Forensic Investigations: The unique features of this bone make it valuable in forensic investigations, aiding in the identification of human remains.
VII. Surgical Procedures
A. Bone Reconstruction: Severe trauma or congenital deformities may necessitate frontal bone reconstruction procedures to restore both functionality and appearance.
B. Trephination and Craniotomy: Historical practices involving drilling holes into the skull, trephination, and craniotomy were used to address various medical conditions.
VIII. Interesting Facts
A. Use in Age Estimation: Anthropologists and forensic experts utilize the frontal bone to estimate a person’s age at the time of death, providing valuable insights in forensic contexts.
B. Cultural and Historical Significance: Throughout history, this bone has held cultural and historical significance, finding its place in ancient rituals, artworks, and human identity.
Questions:
What is the main function of frontal bone?
The primary function of frontal bone is to protect the brain from potential external injuries. It forms the front of the cranium, contributing to the overall structural integrity of the skull.
2. What are some common conditions associated with the frontal bone?
Fractures are common conditions affecting the frontal bone, usually resulting from traumatic accidents. Additionally, frontal sinusitis, an inflammation of the frontal sinuses, can cause discomfort and require medical attention.
3. How does the frontal bone develop during fetal growth?
During fetal development, the frontal bone forms from separate bones that fuse together. This process showcases the intricate nature of human growth and development.
4. How do diagnostic techniques help assess frontal bone issues?
Medical imaging techniques like X-rays and CT scans are used to diagnose frontal bone fractures and assess sinus conditions. MRI scans provide detailed images for a comprehensive understanding of any frontal bone-related issues.
5. Are there any cultural or historical significances associated with the frontal bone?
Yes, the frontal bone has featured in cultural practices, artworks, and ancient rituals, signifying its historical importance and its role in shaping human identity and art throughout history.
Related Articles
Cubital fossa : Anatomy, Borders, Contents
Posterior triangle of neck : Borders, Contents, Divisions, Mnemonics
Study More