Table of Contents
Quick overview:
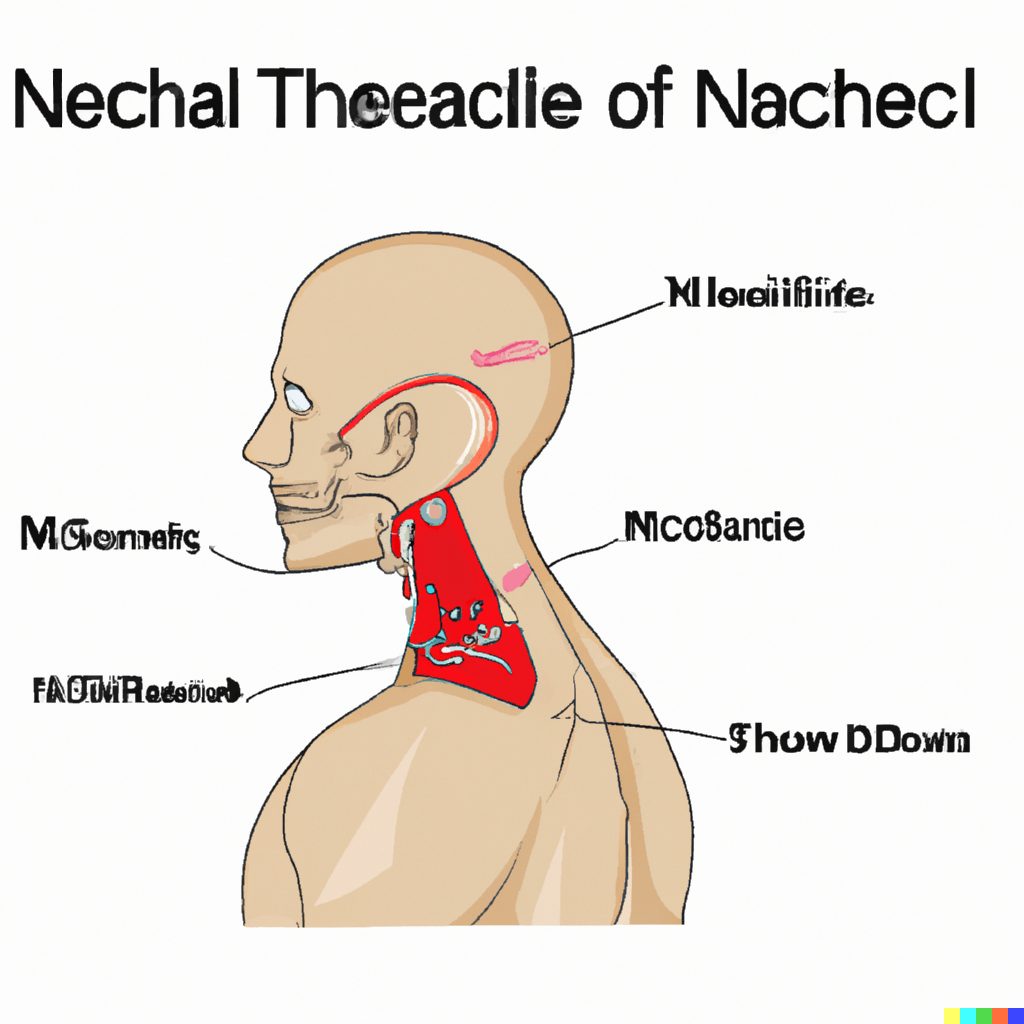
The posterior triangle of the neck in the human body is that region which is located in the posterior aspect of the neck, and bordered by the sternocleidomastoid muscle, the trapezius muscle, and the clavicle bone. This area contains the important structures of the body, such as nerves, arteries, veins, and lymph nodes.
The posterior triangle of the neck can be subdivided into two smaller triangles i,e the occipital triangle and the supraclavicular triangle, which are formed by the omohyoid muscle.
The occipital triangle contains important structures of the body such as, the accessory nerve, the occipital artery, and the suboccipital lymph nodes. The supraclavicular triangle contains the brachial plexus, the subclavian artery, and the supraclavicular lymph nodes.
There are various pathologies that can affect the posterior triangle, such as tumors, infections, and other congenital anomalies. These conditions can cause pain, swelling, and dysfunction of the structures in the area.
Understanding the anatomy and the potential pathologies of the posterior triangle of the neck is very crucial for healthcare professionals to provide effective diagnosis and treatment for their patients.
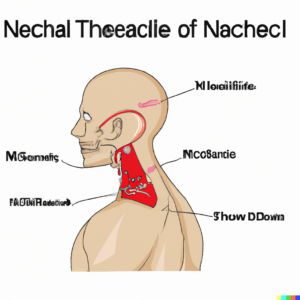
Borders of posterior triangle of neck:
The borders of the posterior triangle of the neck formed by these structures;
Anterior border: It is formed by the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
Posterior border: It is formed by the anterior border of the trapezius muscle.
Inferior border: It is formed by the middle third of the clavicle.
Contents of Posterior triangle of neck:
The posterior triangle is located in the lateral aspect of the neck, and bounded by the several anatomical structures. The contents of the posterior triangle of the neck are given as:
1- Muscles: The triangle contains several muscles, which are the trapezius, the levator scapulae, and the omohyoid muscles.
2- Arteries: The triangle contains several important arteries such as the subclavian artery which passes through the posterior triangle and gives off several branches, including the transverse cervical artery, suprascapular artery, and occipital artery.
3- Veins: The veins of the triangle, include the external jugular vein and the posterior cervical vein. The subclavian vein passes through the posterior triangle and joins the internal jugular vein to form the brachiocephalic vein.
4- Nerves: The posterior triangle of the neck contains the brachial plexus and several other nerves, including the spinal accessory nerve, lesser occipital nerve, and great auricular nerve, pass through the posterior triangle.
5- Lymph nodes: The posterior triangle also contains several lymph nodes, including the supraclavicular lymph nodes and the occipital lymph nodes.
Posterior triangle of neck contents mnemonic:
It’s hard to remember the contents of the triangle for a longer period of time, in this case mnemonic helps us to remember the name of these structures easily. A commonly used mnemonic to remember the contents of the posterior triangle of the neck is:
“Emma’s Soup Made Aunt Lucy Perky Tea”
Each letter of this phrase used to describe a different structure in the posterior triangle:
Eemma’s (E) for = External Jugular Vein
Soup (S) for = Spinal Accessory Nerve
Made (M) for = Middle Scalene Muscle
Aunt (A) for = Accessory Nerve (XI)
Lucy (L) for = Lesser Occipital Nerve
Perky (P) for = Phrenic Nerve
Tea (T) for = Transverse Cervical Artery
Subdivision of posterior triangle of neck:
The posterior triangle of neck is subdivided in to two smaller triangles by the omohyoid muscle which are;
1- Occipital triangle
2- Supraclavicular triangle
1- Occipital triangle:
The occipital triangle is also known as the lateral triangle of the neck or the lesser triangle, a smaller triangular region located in the posterior aspect of the neck, superior to the omohyoid muscle. It is surrounded by the sternocleidomastoid, the trapezius, and the inferior belly of the omohyoid muscle. It contains various important structures such as nerves, arteries, and lymph nodes.
Occipital triangle borders:
Anterior border: Its formed by the posterior border of sternocleidomastoid muscle
Posterior border: It is formed by the anterior border of trapezius muscle
Inferior border: It is formed by the middle third of clavicle
Occipital triangle content:
1- Accessory nerve (CN XI): The accessory nerve passes through the occipital triangle, and descends along the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle before entering the muscle.
2- Cervical plexus: The cervical plexus is a complex network of nerves located in the cervical region. The nerves here arise from the ventral rami of the first four cervical nerves. It supplies the skin and muscles of the neck and shoulder region.
3- Transverse cervical artery: This artery arises from the thyrocervical trunk and supplies to the trapezius and other muscles in this area.
4- Suprascapular artery: This artery passes through the occipital triangle and supplies blood to the supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles and arises from the thyrocervical trunk.
5- Lesser occipital nerve: This nerve passes through the occipital triangle and supplies the skin of the posterior scalp and neck.
2- Supraclavicular triangle:
The supraclavicular triangle, also called the omoclavicular triangle, is a small triangular area located between the clavicle (above) and sternocleidomastoid muscle (below). It is formed by the intersection of three structures i,e the clavicle bone, the sternocleidomastoid muscle, and the trapezius muscle.
Borders of Supraclavicular triangle:
Superior border: It is formed by the inferior belly of omohyoid
Anterior border: It is formed by the posterior edge of sternocleidomastoid muscle
Inferior border: It formed by the clavicle
Content of Supraclavicular triangle:
Subclavian artery: This is the major artery of the upper limb and its function is to supply blood to the arms and upper body.
Subclavian vein: This is the major vein of the upper limb and its function is to drain blood from the arms and upper body and return it to the heart.
Brachial plexus: This is a complex network of nerves that originates from the cervical region of spinal cord and provides motor and sensory innervation to the upper limbs.
Lymph nodes: The supraclavicular lymph nodes located in the posterior triangle of the neck and drain lymphatic fluid from the head and neck.
Thoracic duct: The thoracic duct is the largest lymphatic vessel in the body. It drains the lymphatic fluid from the lower body and left upper body into the left subclavian vein.
Case Study:
Watson, a 40 years old patient presents with pain and weakness in their right arm. Upon examination, you notice an enlarged lymph node in the posterior triangle of the neck on the right side. What other structures should you examine in the posterior triangle of the neck, and what possible causes could explain the patient’s symptoms?
Practice MCQs on Posterior triangle of neck:
1- Which muscle forms the anterior border of the posterior triangle of the neck?
a) Sternocleidomastoid
b) Trapezius
c) Levator scapulae
d) Rhomboid major
Answer: a) Sternocleidomastoid
2- The major nerve that runs through the posterior triangle of the neck and provides motor innervation to the trapezius and sternocleidomastoid muscles?
a) Accessory nerve
b) Hypoglossal nerve
c) Vagus nerve
d) Facial nerve
Answer: a) Accessory nerve
3- The transverse cervical artery, which arises from the thyrocervical trunk, is a major arterial supply to which muscle in the posterior triangle of the neck?
a) Trapezius
b) Levator scapulae
c) Splenius capitis
d) Sternocleidomastoid
Answer: a) Trapezius
4- The structure runs deep to the anterior border of the posterior triangle of the neck is?
a) Subclavian vein
b) Brachial plexus
c) Spinal accessory nerve
d) Transverse cervical artery
Answer: c) Spinal accessory nerve
5- Enlarged lymph nodes in the posterior triangle of the neck may indicate the condition?
a) Carotid artery stenosis
b) Thyroid cancer
c) Esophageal cancer
d) Infection or malignancy in the head and neck region
Answer: d) Infection or malignancy in the head and neck region
Related:
Calot’s triangle: Anatomy, Contents, Boundaries
Hesselbach triangle: Anatomy, Border, Content
Cubital fossa : Anatomy, Borders, Contents
Read more